Property Geek
We provide the actual and accurate information with unbiased user driven reviews to our viewers, to help them see the best and find the best!
View posts
Electrical cables are the backbone of any electrical system, enabling the safe and efficient transmission of power and data. With various types of cables available, each designed for specific applications, understanding their differences is crucial for safety, performance, and durability.
Choosing the wrong type of cable can lead to inefficiencies or even hazardous situations. In this article, we’ll explore the different types of electrical cables, their features, and their applications, helping you make informed decisions for your electrical projects.
Some of the labels or identifications that are regularly written on cables are THHN, THWN, THW, and XHHN. Below is a list of the labels’ respective letter meanings.
Not all devices use a similar type of cabling. Having a knowledge of the different types of cables will assist you in having a better insight into what’s going on inside the electrical appliances around you or where and how your electricity reaches you.
Depending on the applications of electrical cables there are more than 20 different types of cables. Let’s take a closer look at them. But before that – composition of cables.
Electrical cables are essential components of electrical systems, serving the purpose of transmitting electrical power or signals from one point to another. The composition of types of electrical cables can vary depending on their intended application, but they generally consist of several key components:
The type of cables used for the transmission of signal or in the other words, for communication purposes is called communication cables. They can be of three subtypes.

Coaxial cables are made of 4 layers forming the coaxial structure (i.e., having a common center or axis). The central layer is the conductor. The surrounding layer which is the second layer is the insulating plastic. These two layers are encased in a metallic sheath. The last layer is the outer insulating plastic. Amongst the different types of cables, coaxial cable is used to transmit high frequencies with very low noise interference (achieved by the presence of metallic sheath). It is used in cable television, satellite communications, and high-speed internet access.
| Types | Uses | Cost (depending on length) |
| Hardline coaxial/Heliax cable | Connects transmitter and aerial antenna | Rs.50 – Rs. 700 |
| Radiating or Leaky coaxial cable | Connects transmitter and underground antenna | Rs.10 – Rs.5000 |
| RG 6 coaxial cable | Cable television, internet connection, house wiring | Rs.10 – Rs.40 |
| Twinax coaxial cable | 10 GB Ethernet network, LAN | Rs.500 – Rs.11000 |
| Triax coaxial cable | Television industry to connect camera and CCU | Rs.10 – Rs.50 |
| Semi-rigid coaxial cable | Test equipment, aerospace applications, PIM, medical | Rs.10 – Rs.1300 |
| Rigid line coaxial cables | Indoor applications, TV, and FM | Rs.10 – Rs.1300 |
| Twisted pair cable | Ethernet, telephone, DSL lines | Rs.10 – Rs.10000 |
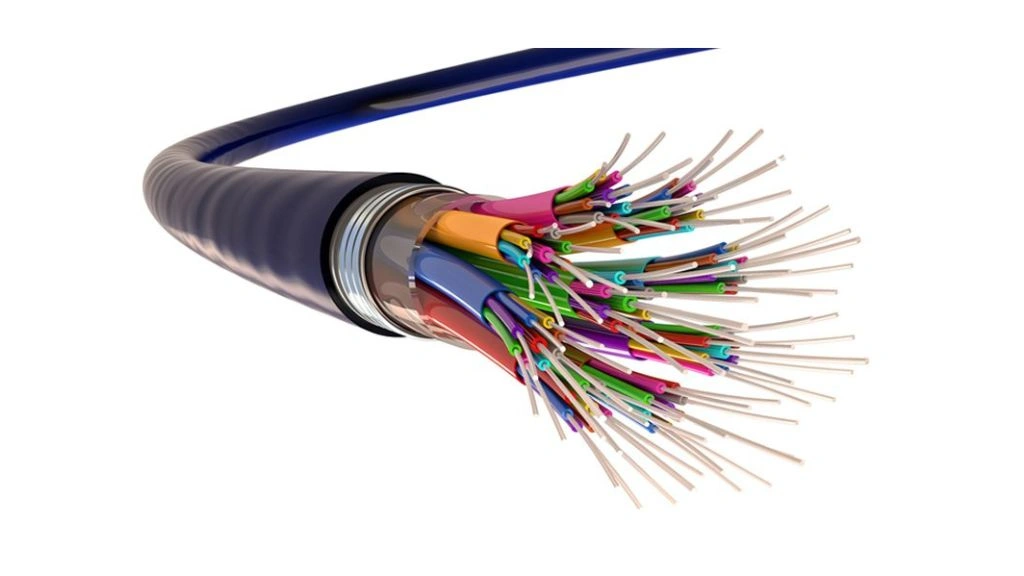
Fiber optic cable is one of the different types of cable. It is made of transparent and flexible glass fibers called optical fibers. These optical fibers transmit data in the form of light. The thickness of each optical fiber is similar to the thickness of human hair. Relatively new to the market, fiber optic cables are not yet used in households. Since it employs rapid pulses of light to transmit data, its speed is unimaginably faster than any standard copper wire.
| Types | Uses | Cost (approx.) |
| Single-mode or mono mode optical fiber | Long-distance communication | Rs.200 |
| Multi-mode fiber optic | LAN security systems, the short-distance communication application | Rs.500 – Rs.1000 |
Direct-buried cable is yet another cable amongst the different types of cables. It is designed specifically to be buried underground without any extra insulation. It has water-resistant protection, plastic insulation, and other protection for underground factors that would otherwise affect any other normal cable.
| Uses | Cost (approx.) |
| Underground cabling in a wet or dry environment | Rs.50 – Rs.300 |

The outer insulating of the non-metallic cable is made of plastic. These cables are of two types depending on the number of conductors used. Two wires NM-sheathed conductors have two conductors separately insulated and a conductor for ground. Thus, a total of three conductors exist. A Three-wire NM-sheathed conductor has three conductors that are separately insulated with a third conductor for ground.
| Types | Uses | Cost (approx.) |
| Two wires NM-sheathed cable | Residential electrical wiring | Rs.4000 |
| Three wires NM-sheathed cables | Residential electrical wiring with three-phase connection |

A metallic sheathed cable is a type of cable with metallic protection over the plastic insulated conductors. These cables are of two types: armored cables and metal-clad cables.
| Types | Uses | Cost (approx.) |
| Armored cables (AC) | Supply mains electricity or large appliances in dry locations | Rs. 58000 |
| Metal-clad cables (MC) | Supply mains electricity or large appliances in wet or underground locations |
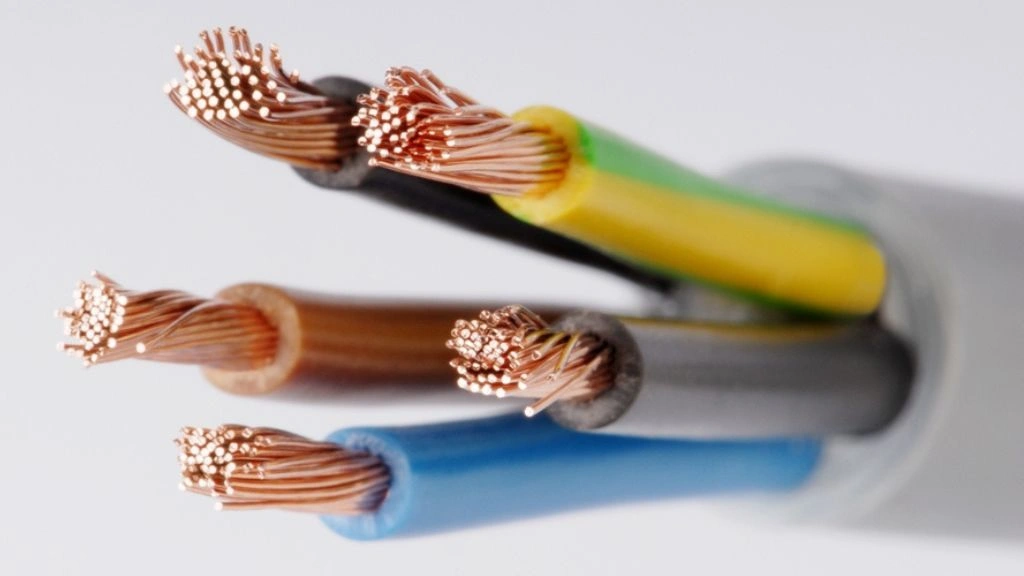
Amongst the different types of cables, the multicore cable is the type that has more than one number of conductors with insulated protection rolled into one jacketed cable. It avoids messy connections by having one compact cable instead of ten or twenty separate wires. Using a multicore cable is a time saver as all the wires can be connected at the same time.
|
Types |
Uses |
Cost (approx.) |
|
Shielded multicore |
Sending and receiving audio and video signals, TV studios, CCU |
Rs. 100 – Rs. 2000 |
|
Unshielded multicore |
| Types | Uses | Cost (approx.) |
| Shielded multicore | Sending and receiving audio and video signals, TV studios, CCU | Rs. 100 – Rs. 2000 |
| Unshielded multicore |
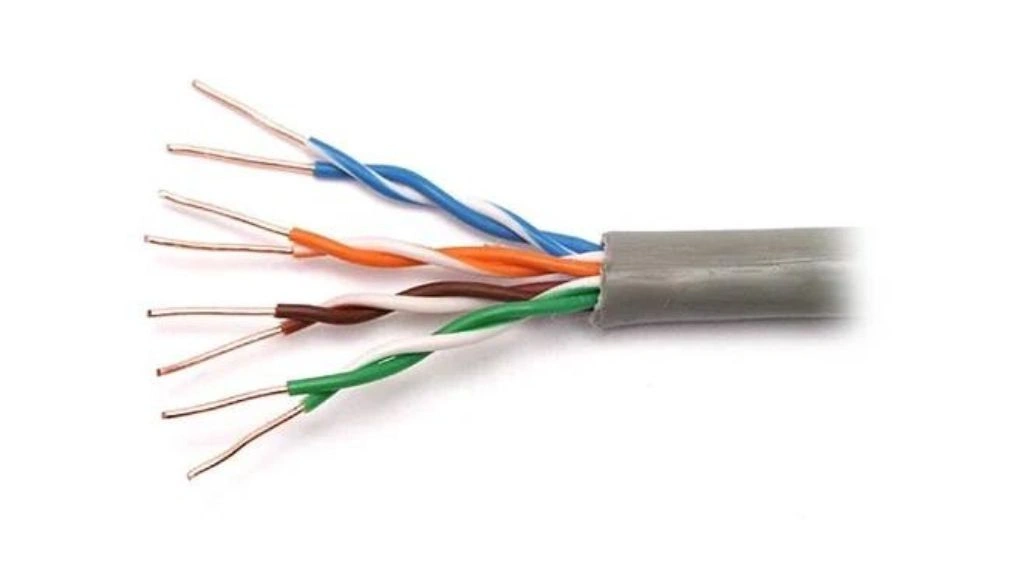
Paired cables are a pair of two insulated conductors encased in an insulation sheath.
| Types | Uses | Cost (approx.) |
| Twisted pair cable | DC applications, low-frequency AC applications. | Rs.100 – Rs. 1500 |
| Bonded pair cable |
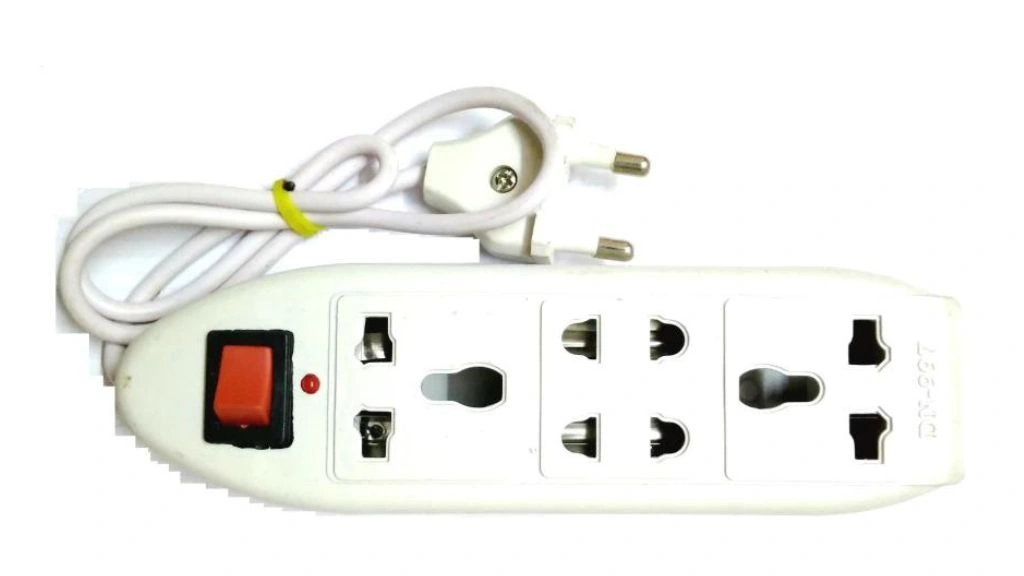

It is an electrical cable that is flexible having connectors on both ends that provide a temporary AC power supply. It is usually used as an extension of the power source to portable appliances.
| Uses | Cost (approx.) |
| Helps in connecting portable devices from a power supply located at a distance. | Rs.200 – Rs.3000 |
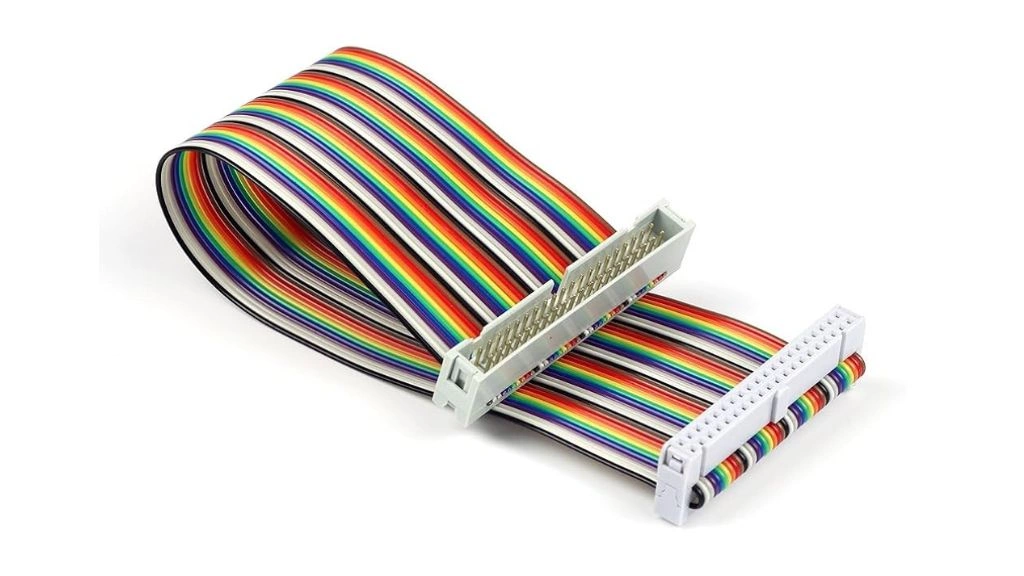

Ribbon cables are unique cables amongst the different types of cable, shaped like a ribbon. It’s made of multiple small grades of insulated wires placed parallel to each other in a flat shape.
| Uses | Cost (approx.) |
| Connects the internal peripherals in computers or electronic devices | Rs.60 – Rs.5000 |
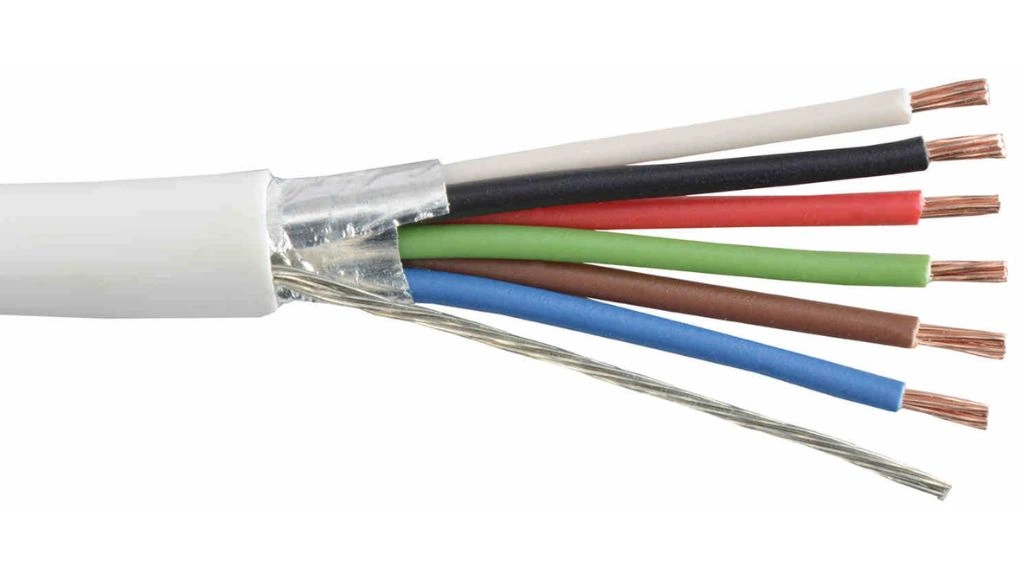

In screened cables, the conductors are encased in a metallic layer known as a shield. The shield is made from copper, braided aluminum, or any other metal. It could also be a solid layer, a foil, or a spiral tape made from the above-mentioned conducting metals.
| Uses | Cost (approx.) |
| data can be transferred without degradation by EMI exposure | Rs.30 – Rs.200 |
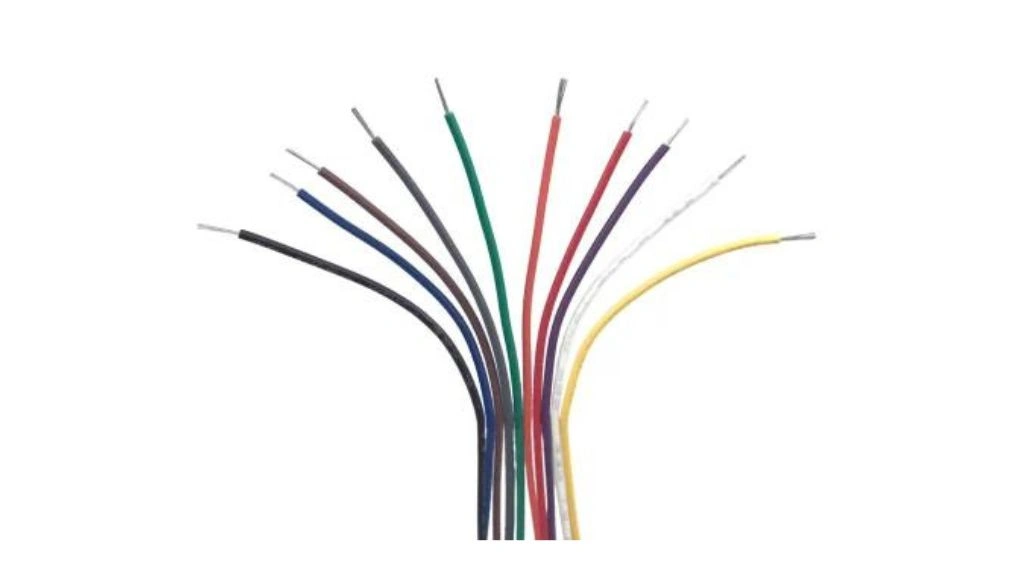

Amongst the different types of cables, single-conductor wire is yet another type. It is made of a single insulated conductor. They are available in multiple colors so as to identify phases and earth lines. The single-stranded wire and the single-solid wire are two subtypes.
| Types | Uses | Cost (approx.) |
| Single Stranded Wire | applications where wires are required to be twisted or bent. | Rs.60 – Rs.4000 |
| Single Solid Wire | applications where there is no movement or bending of wires. | Rs.250 |

Submersible cables are useful under submerged conditions, as the name suggests. Its insulation is abrasion-resilient, very rugged, and highly durable. Submersible cables have two different types as mentioned below.
| Types | Uses | Cost (approx.) | |
| Single-core | flat | supplies power for drilling purposes, to submersible motors and pumps, in agriculture industries, or underground mining | Rs.2000 |
| round | |||
| Multiple cores | flat | ||
| round | |||
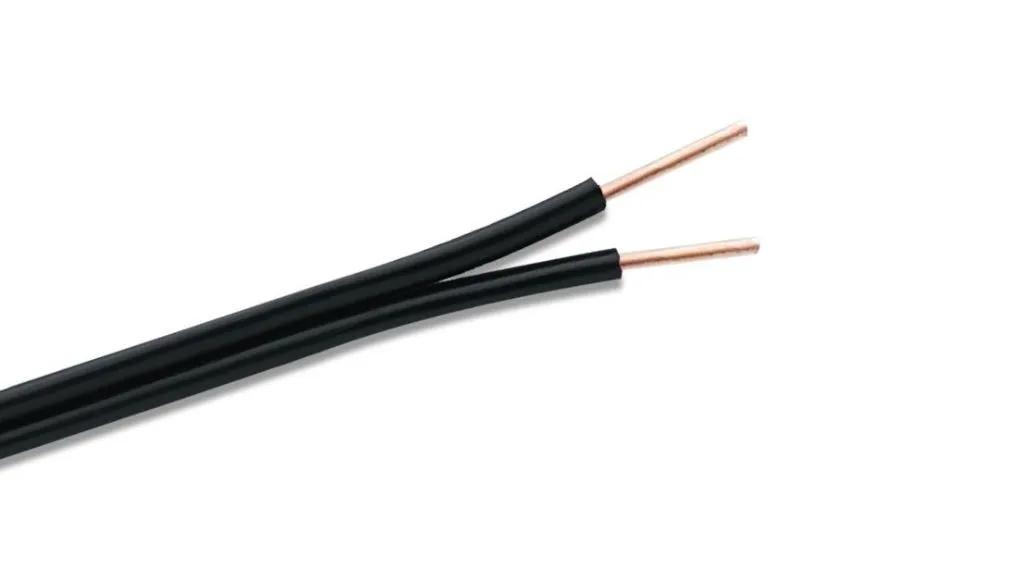

Twin lead cables have two conductors held apart and placed uniformly by a plastic layer in between them. Signal distortion is due to unequal speaking so equal spacing of the two conductors is very important.
| Uses | Cost (approx.) |
| Used in applications where low power loss is important, carries RF signals | Rs.1000 |
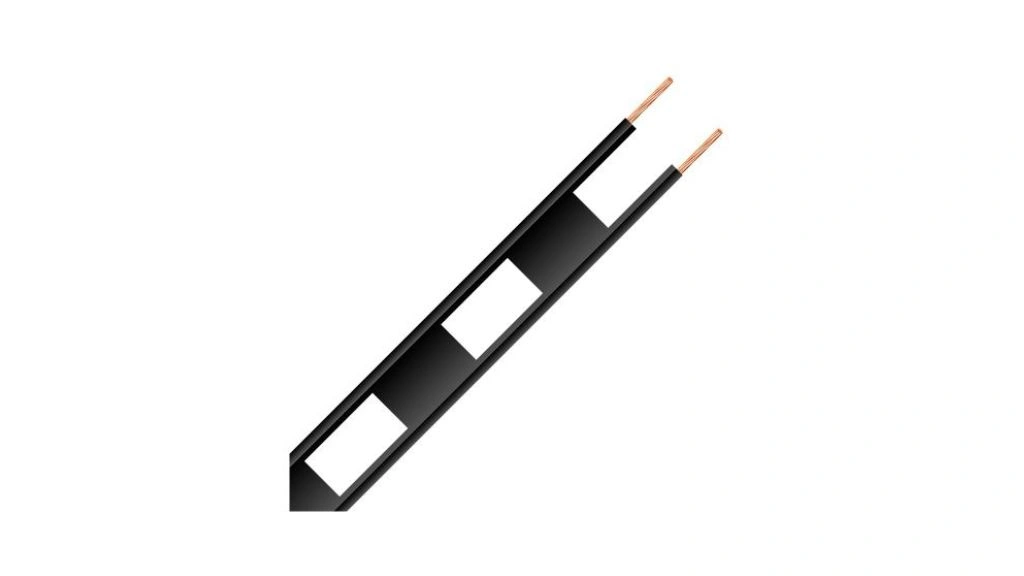

Ladder line cables are important in wet conditions as sometimes wetness seeps inside the plastic covering the conductors. This will cause interference in the signal. To avoid such interference, slots like a window are cut into the plastic layer. The wire thus resulting will resemble a ladder-like structure. Hence, the name ladder line has been coined. The Cost and use of ladder line cable are as given below.
| Uses | Cost (approx.) |
| transmitter or receiver with RF antennas in TV and Radios etc. | Rs.20 |
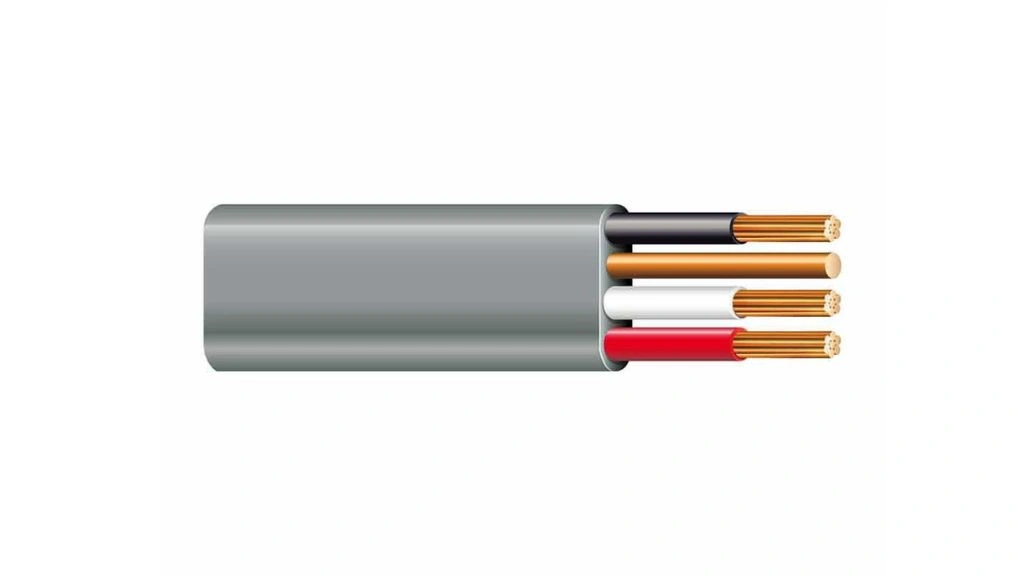
UF cables have conductors that are surrounded by an individual layer of thermoplastic. It provides flexibility and additional protection. The uses and cost of UF cable are as given below.
| Uses | Cost (approx.) |
| supplies power to a lamp post or street light, used in damp locations | Rs.50 – Rs.300 |
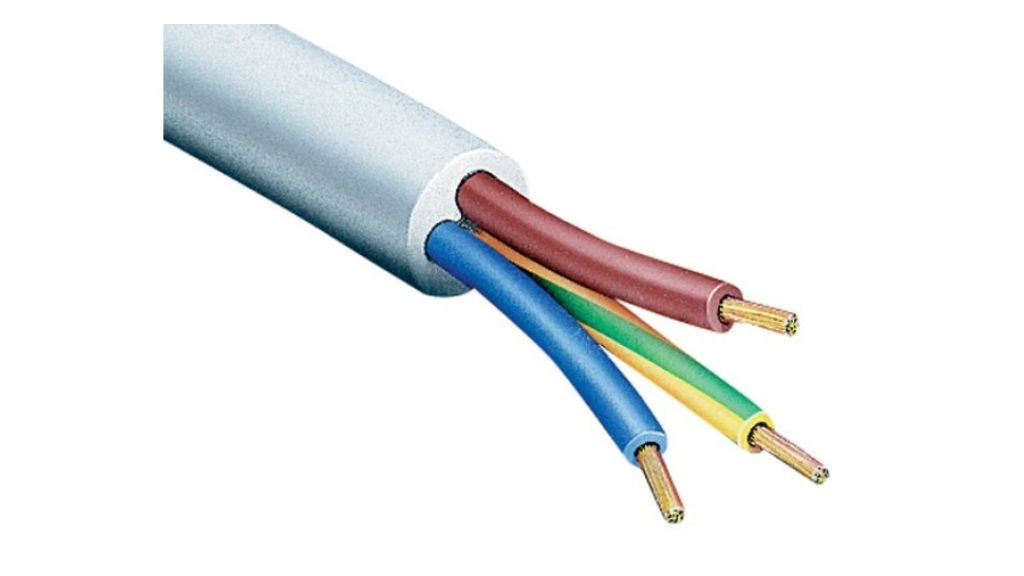
Flexible cables are yet another one amongst the different types of cables. It can withstand continuous bending in moving appliances. The flexibility is obtained by the usage of stranded conductors. Its uses and cost are as given below.
| Uses | Cost (approx.) |
| Used in CNC-based machines like milling machines, engraving, etc., pick and place machines | Rs.50 – Rs.6000 |
The different types of cables also include power transmission cables seen in overhead transmission lines. There are 4 types as is mentioned below.
At the end of this article, you must have come across varieties of different types of cables which are used in both the telecom sector and all households. Identifying which cable goes wire is a bemusing task. This article will help you to not all identify such perplexing cables but also their cost, applications, and structure. The types of cables that exist both in the layman’s world and in the telecommunication sector have been briefed above.