Property Geek
We provide the actual and accurate information with unbiased user driven reviews to our viewers, to help them see the best and find the best!
View posts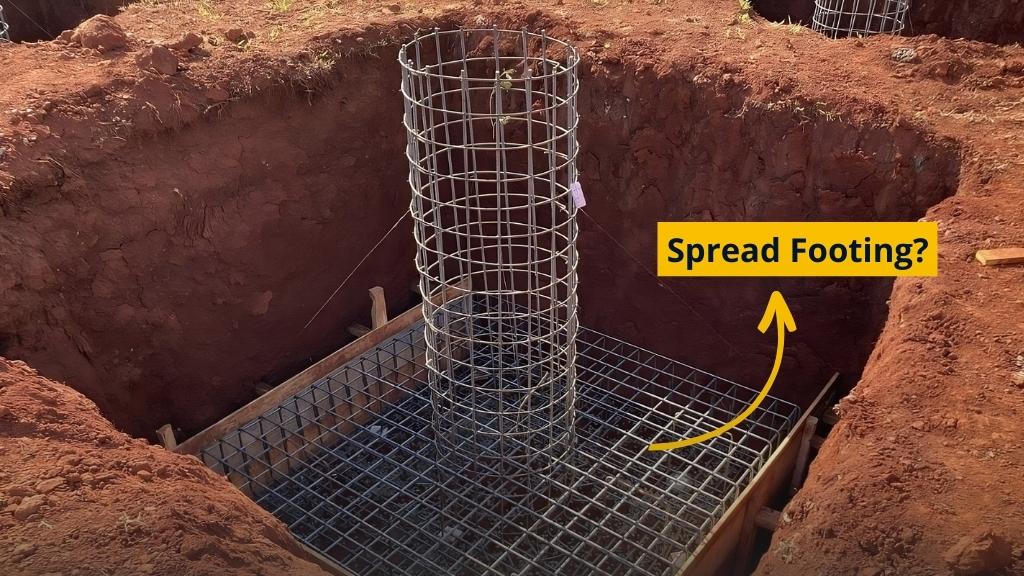
The spread footing is utilized to transport and distribute the load arriving to the formation to the soil underneath it as well as to support the column and walls of the building.
When there is symmetric footing, this form of footing is frequently a stiff element, and they are orthogonal by default. This foundation really acts like an inverted cantilever when weights are applied upward.
This kind of foundation can take the shape of a slab that is homogeneous in thickness and can be round, square, or rectangular; it may also be stepped to assign the weight over a wide area.
In comparison to the base of a load-bearing foundation, spread footings are a little bit broader. This is also known as a spread foundation with steps.
This type of footing consists of the construction of an RCC member-based base foundation. This deeper bottom spreads the weight across a larger area, which strengthens the structure.
Since they are designed differently from conventional spot footers, the spread footings are made of concrete and steel and are less prone to fail.
The article below covers everything you need to know about spread footing.
The building industry frequently use the spread foundations. For individual support, the structure’s base enlarges or spreads. Read below to know the varied types of spread footing foundation.

In essence, a raft foundation, also known as a mat foundation, is a continuous slab sitting on the ground that covers the whole footprint of the structure, supporting it and dispersing its weight to the ground.
Raft foundation is basically a combined footing that covers the entire region immediately beneath a structure and supports all the walls and columns.
An R.C.C. slab of the appropriate thickness is supplied in this foundation, either with or without a beam.
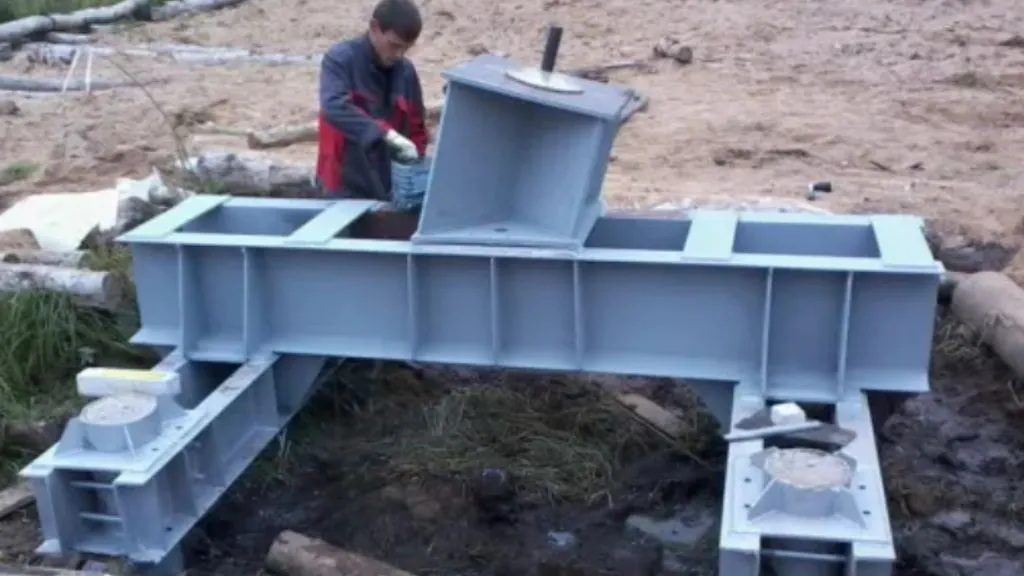

A foundation for grilling is made out of one, two, or more levels of beams (usually made of steel) layered on top of a concrete layer to distribute the weight over a vast area. Usually, heavy-structured pillars and column scaffolds employ this kind of base.
When using low-bearing-power soils, a grillage footing is used to transfer heavy loads from the steel column.
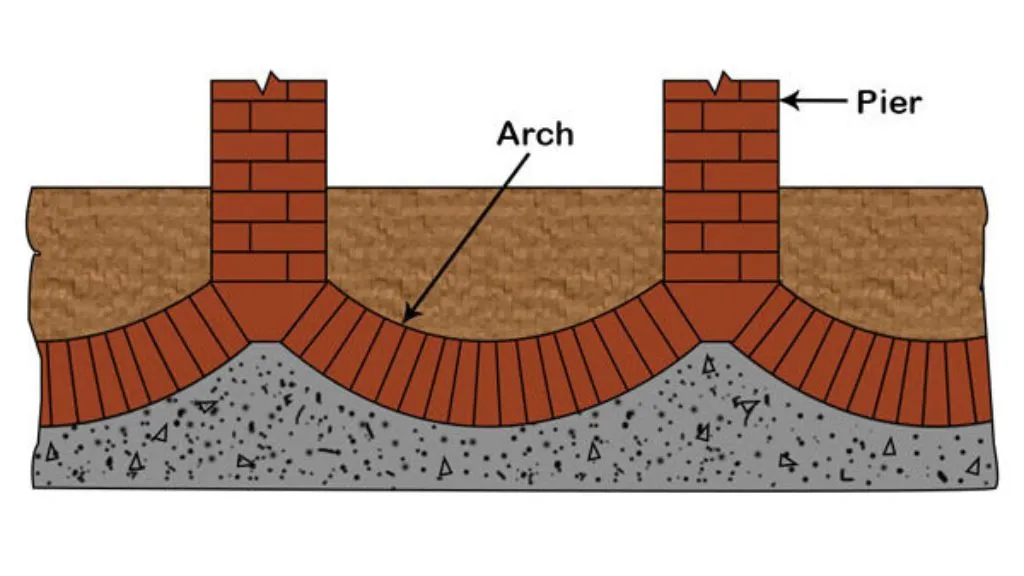
When compared to a typical arch bridge, an inverted arch, also known as an invert, is a civil engineering construction. The arches merely disperse the downward loads of the viaduct piers onto a larger ground surface, much like an inverted arch bridge, in the simplest case.
This type of foundation is used in locations where the soil’s bearing capacity is extremely low, the load of the building is concentrated on the walls, and extensive excavations aren’t feasible.
When more than two columns are supported, the footing is said to be continuous. The footing is comparable to a wall‘s strip footing. When the weights are heavy, a longitudinal beam that runs lengthwise is used to transmit the loads from the individual columns instead of straight to the foundation slab.
This kind of foundation reduces differential settling and is appropriate for earthquake-prone areas.
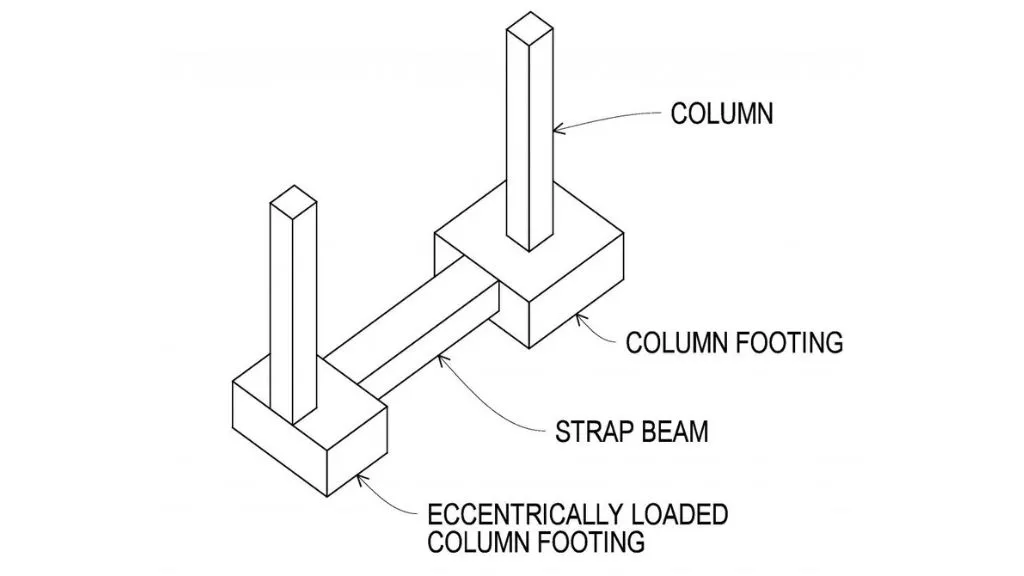
A strap footing is a component of a building’s foundation. A concrete beam linking two or more column footings makes up this type of composite footing. This type of beam includes strap beams.
A strap footing is composed of two or more independent footings connected by a strap beam. Other names for it are pump handle foundation and cantilever footing.
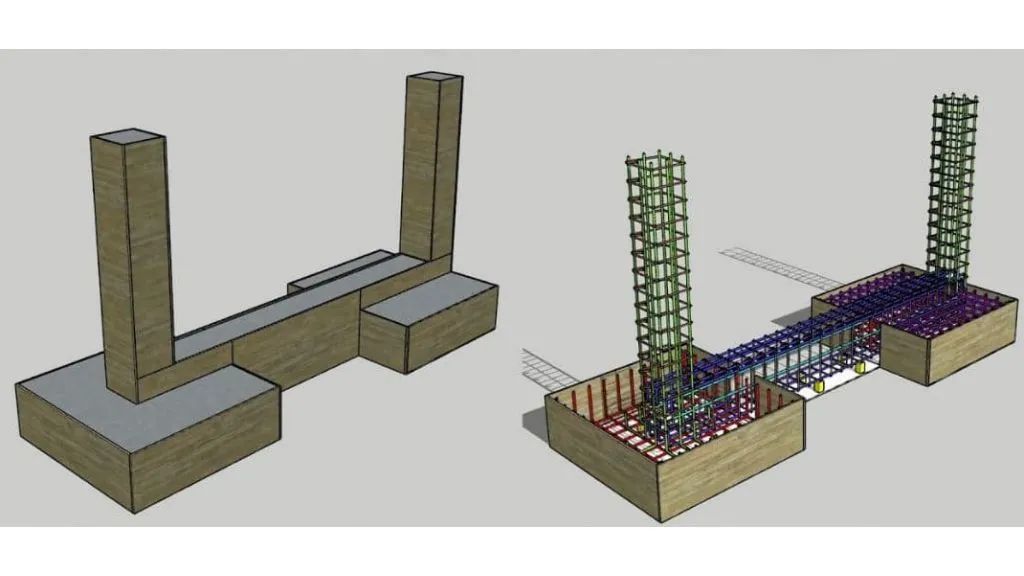
A strap footing is a component of a building’s foundation. A concrete beam linking two or more column footings makes up this type of composite footing. This type of beam includes strap beams.
A strap footing is composed of two or more independent footings connected by a strap beam. Other names for it are pump handle foundation and cantilever footing.
The term “mixed footing” or “combined footing” refers to when a single footing must handle two columns, or in rare circumstances more. We give a single foundation for two or three columns that are situated quite close to one another, and the footing is referred to as a combined footing.
This type of footing is created when two or more columns are present in a row. There are two different types of footing in this:
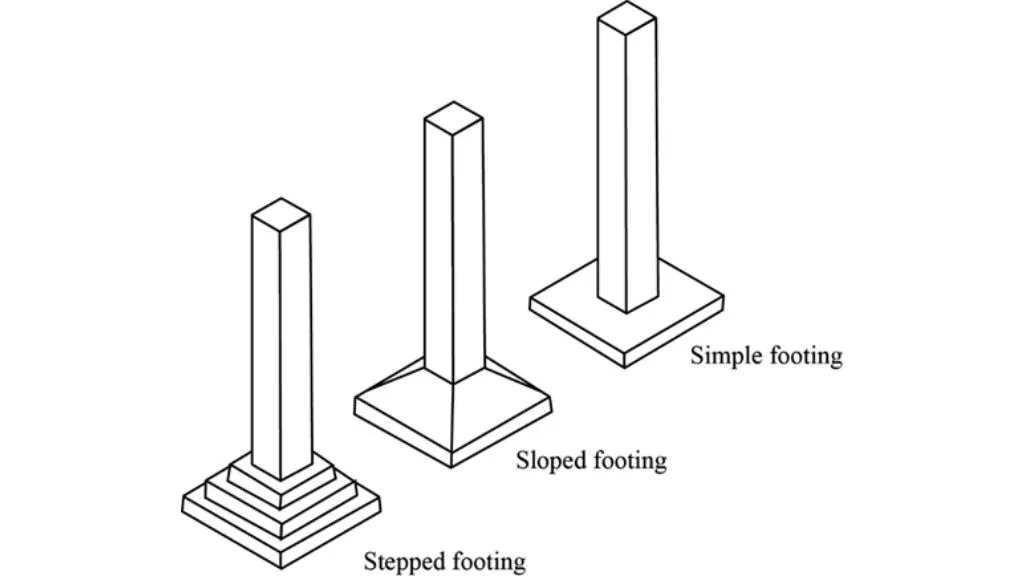
The single or individual footing known as an isolated footing is what distributes weight to the subsurface earth. When a single column is required, it is given. The portion of the substructure that rests inside the ground or has direct contact with it is known as the foundation.
For a single column, this style of footing is used. These three forms of isolated footing are further divided into:
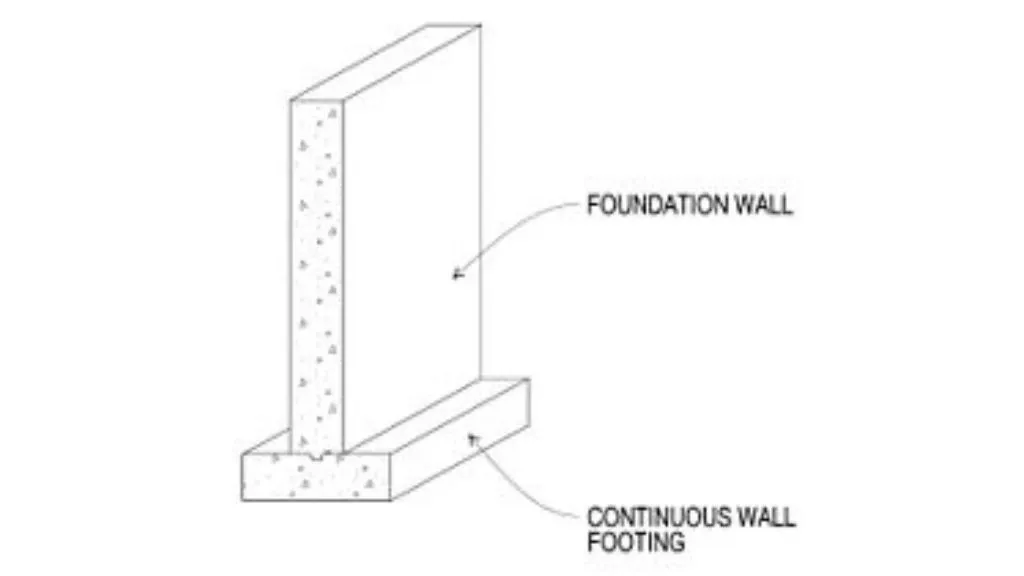
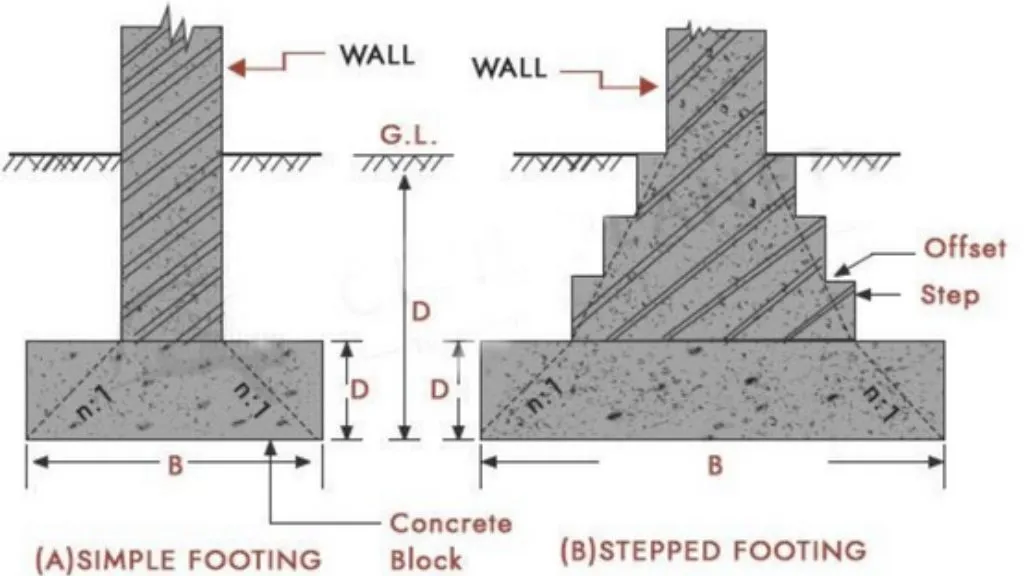
A continuous strip of concrete known as a wall footing or strip footing is used to distribute the weight of a load-bearing wall over a soil area. It is an essential part of a thin foundation. Both reinforced concrete and ordinary concrete can be used to build wall footings that support direct vertical loads.
Most wall footings are either straightforward or steep. Wall footing can also be divided into two categories:
The footing’s depth needs to be adequate to adequately withstand punching shear and direct shear caused by column stress. The reinforcement for the footing should also be constructed to withstand bending moments.
The dowels that are offered at the column-footing interface should be able to transmit column load. Spread footings are built using concrete and steel reinforcement for added stability.
The benefits of spread footing include,
It is referred to as a shallow or stepped foundation if the depth of the foundation is less than the breadth of the foundation.
Instead than using a subterranean layer or a variety of depths as in a deep foundation, a shallow foundation essentially distributes building weights to the soil extremely near to the surface.
When building a structure on soil that must have a maximum bearing capacity, this method may be utilised. This Foundation has a minimum depth of 800 mm and a maximum depth of 4 metres.